The web is moving from HTTP 1 to HTTP/2. Not sure what HTTP/2 is yet? No worries, today we’ll discuss it in depth.
First, What is HTTP?
HTTP is a short for Hypertext Transfer Protocol; something that manages the communication between the browser on your computer and the web servers, where a website is hosted.
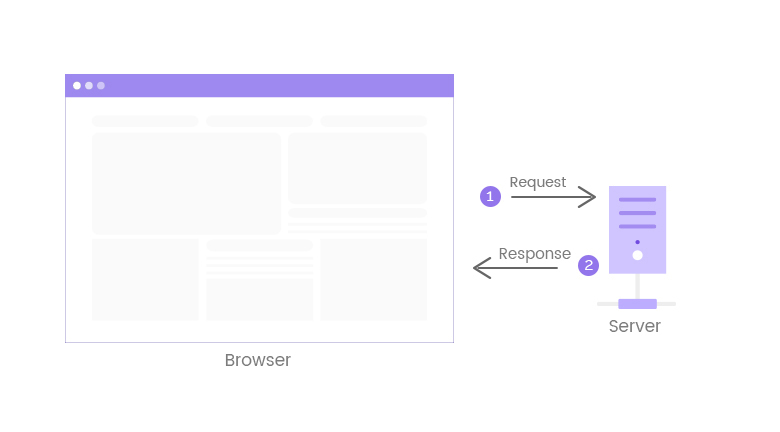
To describe it in even simpler language, HTTP is how browsers and servers talk to each other. When you enter any URL in the browser, it sends an HTTP request to the server asking for the web page and files associated with it.
HTTP was originally proposed by Tim Berners-Lee; and later released in 1991 with simplicity in mind. Even though Internet has evolved a lot since then, HTTP, the backbone of the Internet underwent very few improvements.

Surprising isn’t it?
How Does HTTP 1 work?
HTTP 1 versions are limited to processing only one request at a time.
If you remember the old websites of the 90s, they were pretty simple. Mostly one HTML file per web page; like index.html for the home page, contact.html for contact page and so on. No external CSS files, No JavaScripts libraries or anything of that sort. So even though, earlier HTTP version were limited to processing only one request at a time, it did not really matter much then.
But now Internet has changed and websites have become complex. Along with the HTML file, browsers need to load several external CSS stylesheets, JavaScript files, tons of media and image resources to open a single web page.
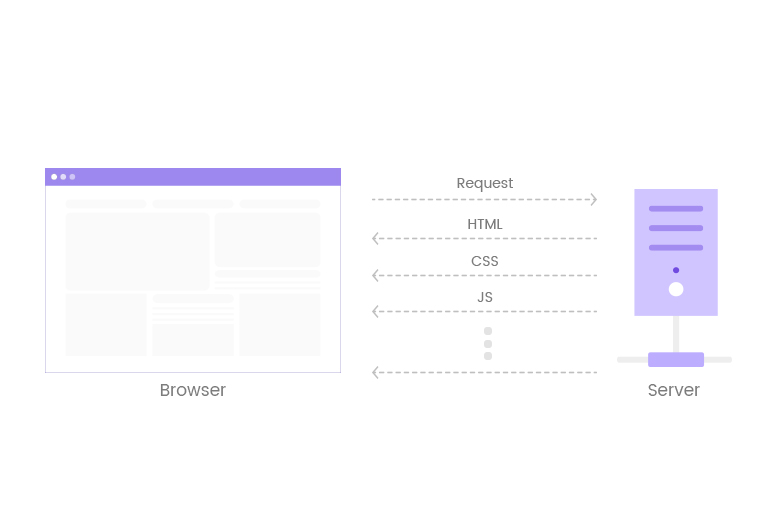
So for the websites still on HTTP 1 versions, browsers are forced to open multiple connections in parallel to process multiple requests simultaneously. However too many connections in parallel may cause the congestion. Modern browsers process about only 6 parallel requests.
If there are more than 6 requests needed to load a webpage, they are queued and hence, users experience slow page load times.
How Does HTTP/2 Work?
HTTP/2 was released in 2015 considering the needs of the modern web. It’s the first major improvement to the HTTP after 1997; heck good 18 years!
Below are just some of the noteworthy features of HTTP/2:
- Multiplexing
- Header Compression
- Server Push
All these features are primarily focused around performance and security. But the one that’s my favourite is Multiplexing.
Multiplexing allows multiple requests to be active at once. So unlike processing only 6 requests parallely and putting the rest in the queue as seen in the previous example; HTTP/2 can send unlimited HTTP requests with just one connection.
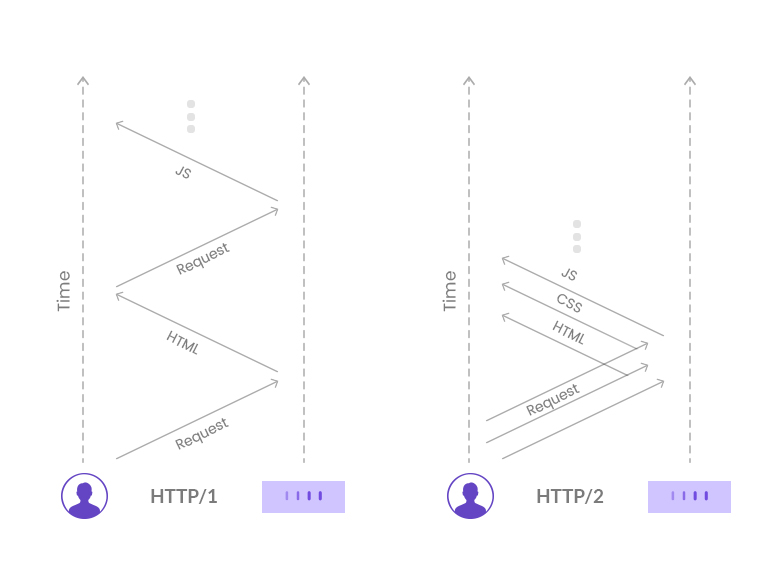
This immediately improves performance and speed of the websites drastically. As seen in many, many tests, HTTP/2 can load 2x faster!
How to get started with HTTP/2?
The very basic requirement to have your website on HTTP/2 is to have your website on SSL. Once you have SSL installed, you can enable the HTTP/2 in your server configurations.
But if you’re not a techie, you don’t have to worry about it a bit. Just ensure that your website is hosted with companies like Cloudways which support HTTP/2 by default.
Conclusion:
If your website is not on HTTP/2 yet, get it transferred right away. If you’re not sure, you can test it quickly with this tool.
Disclosure: This blog may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through one of these links, we may receive a small commission. Read disclosure. Rest assured that we only recommend products that we have personally used and believe will add value to our readers. Thanks for your support!






Thanks – didn’t know the test-tool by now.
Nice to know for sure, that my pages are HTTP/2 🙂
And thanks for the visual description!
What are other ways if hosted on bluehost
Hello Pramod,
You will need to check once with the Bluehost team. I am sure they can help you with the same! 🙂